Polydextrose is a synthetic polymer of glucose. It is a food ingredient classified as soluble fibre by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as well as Health Canada, as of April 2013. It is frequently used to increase the non-dietary fibre content of food, to replace sugar, and to reduce calories and fat content. It is a multi-purpose food ingredient synthesized from dextrose (glucose), plus about 10 percent sorbitol and 1 percent citric acid. Its E number is E1200. It was approved by FDA in 1981.
Polydextrose is described in its Foods Chemicals Codex (FCC) Monograph as a randomly bonded (the 1,6-glycosidic linkage predominates) condensation polymer of D-glucose, sorbitol, and citric acid. Commercial polydextrose also contains small amounts of free glucose, sorbitol, citric acid, and 1,6 anhydro-D-glucose (levoglucosan). Polydextrose has a broad molecular weight range (162 to 20,000) with 90% of the molecules being between 504 and 5,000 mw. The average degree of polymerization is 12: average molecular weight of approximately 2000. It is 0.1 times as sweet as sugar.



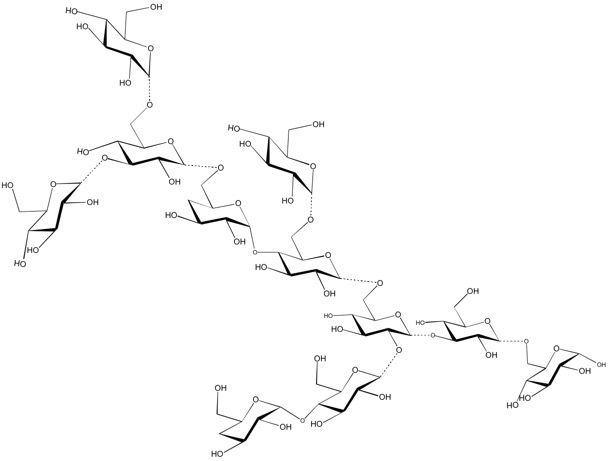 Polydextrose CAS 68424-04-4
Polydextrose CAS 68424-04-4