Glycoscience Products & Services

 Gellan Gum CAS 71010-52-1
Gellan Gum CAS 71010-52-1Gellan is a microbial polysaccharide produced by Pseudomonas elodea and produces gels having similar properties to agar.
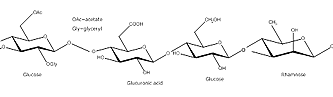
Gellan gum is a linear tetrasaccharide of (1,4)-β-L-rhamnopyranosyl, (1,3)-α-D-glucopyranosyl, (1,4)-β-D-glucuronopyranosyl, (1,4)-β-D-glucopyranosyl- with O(2) L-glyceryl and O(6) acetyl substituents on the 3-linked glucose.
Both substituents are located on the same glucose residue, and on average, there is one glycerate per repeat and one acetate per every two repeats.
In low acyl gellan gum, the acyl groups are removed completely. The high acyl form produces soft, elastic, non-brittle gels, whereas the low acyl form produces firm, non-elastic, brittle gels.