Glycoscience Products & Services

 Guar Gum CAS 9000-30-0
Guar Gum CAS 9000-30-0Guar gum is obtained from the seed of the legume Cyamopsis tetragonolobus, an annual plant that grows mainly in semi-arid regions of India.
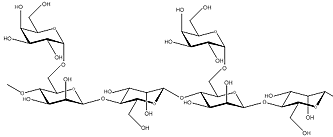
The structure of the polysaccharide consists of a main chain of (1,4)-linked β-D-mannopyranosyl units with single α-D-galactopyranosyl units linked (1,6) on average to every second main chain unit.
Guar has a high viscosity in aqueous solution, shows marked pseudoplastic behaviour and forms synergistic gels in the presence of other gums such as carrageenan and xanthan gum.